Orthopedic Massage
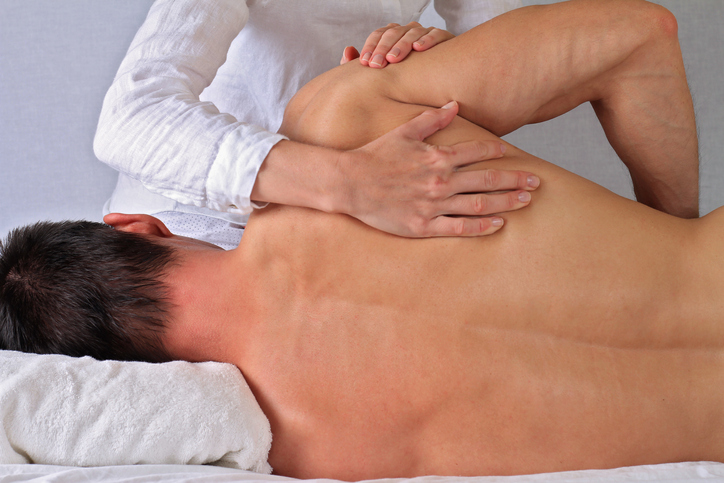

Orthopedic massage is a combination of several manual therapy techniques that create a style of therapy specific to treating severe or chronic orthopedic conditions which affect the soft tissues of the body. This type of massage can be described as a cross between massage therapy and physical therapy. The patient plays an active role during treatment by providing feedback, stretching or engaging in resisted exercises. If you are looking for more out of your massage sessions and want real relief of pain, schedule a Treatment Massage session at Uma Clinic in Seattle.
An Orthopedic Massage Therapist has extensive training. They must understand the condition presented, discern which anatomical structures are involved and what protocols are required to create functional and measurable improvements.
The clinical effects of the Orthopedic Massage are:
- Stimulate the growth of new tissue to promote repair & healing of injuries
- Optimize fluid exchange of blood, lymph and synovial fluids to increase nutrition & oxygenation of the tissue
- Normalizes the function of muscles by reducing hypertonicity in the muscles & strengthening weak muscles
- Restore normal neurologic function in the soft tissue
- Mobilize restricted joints and promote healthy cartilage
- Decrease pain
- Increase mobility and range of motion; restore ease of movement
- Augment productivity in all areas
- Improve athletic performance
- Reduce muscle hypertonicity, tension, and spasm
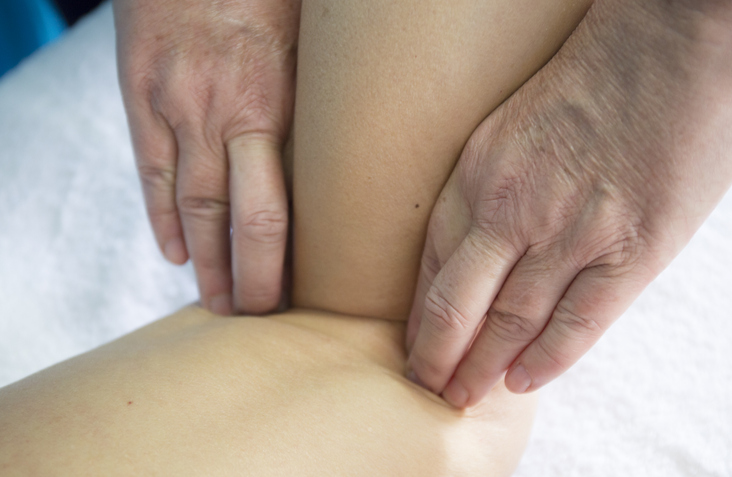
Conditions Benefited by Orthopedic Massage:
- Whiplash
- Headaches
- Tennis/golfers elbow
- Frozen shoulder and rotator cuff injuries
- Sciatica
- Piriformis syndrome
- Iliotibial band syndrome
- Patellar syndrome
- Strains/sprains
- Tendonitis
- Hamstring and quadriceps strain
- Plantar fasciitis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Repetitive strain injuries
- Neck, shoulder, back, hip pain
- Achy/tingling arms, wrists and hands
What other treatments should I complement my treatment with?
To decrease swelling and stagnation consider Manual Lymphatic Drainage. If you have abdominal scaring or issues with gut health, or pelvic dysfunctions consider Abdominal Massage. If you suffer from headaches, jaw pain, JMJ pain consider Intraoral Massage.
We look forward to being part of your Wellness Team! Schedule Treatment Massage in Seattle HERE


